Aortic Occlusive Disease
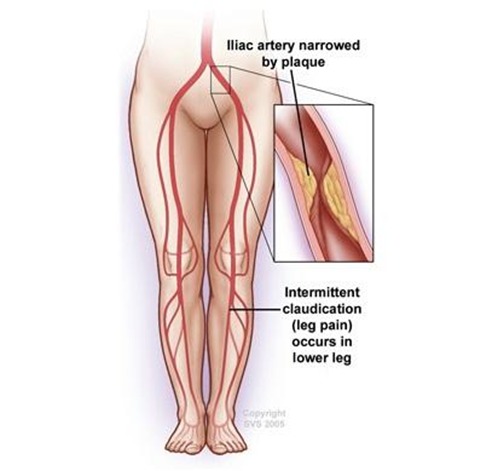
Aortic occlusive disease occurs when blood flow in the aorta is blocked. There are many different health conditions that can cause blockages in the aorta. Aortic occlusive disease can slow or block blood flow to the body's major organs and cause a number of serious health issues.
Symptoms of Aortic Occlusive Disease
The degree of the obstruction and its location in the aorta determine the symptoms of aortic occlusive disease. Depending on how much blood flow is impeded due to the obstruction, symptoms may intensify. Symptoms might appear suddenly and be so severe that immediate medical attention is required. When symptoms are moderate enough, therapy might be postponed until additional diagnostic testing reveals the source of the ailment.
- Arm or leg pain with use (called claudication) or at rest
- Severe high blood pressure
- Stroke
- Abdominal pain when eating
- Other symptoms of organ dysfunction
Risk factors
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- High cholesterol or a high-fat diet, or both
- High blood pressure
- Age over 60
- Family history
Diagnosis of Aortic Occlusive Disease
We use a number of techniques to identify aortic occlusive disease. In addition to using advanced diagnostic imaging to determine the precise location and assess the severity of an aortic blockage, our doctors frequently may reach a diagnosis following a physical examination. Depending on your symptoms, you may undergo a variety of diagnostic tests. These tests may consist of:
- Ankle-brachial index
- Intravascular ultrasound
- CT angiography
- Catheter angiography
Advanced Treatment of Aortic Occlusive Disease
The severity of your disease determines your treatment. Lifestyle modifications and drugs can help you manage your disease and reduce its growth in some situations.
If lifestyle modifications and drugs are insufficient, you may require:
- Bypass surgery:
- Stent placement:
This procedure creates a new channel for your blood to travel around the constricted or obstructed area. This is similar to a coronary artery bypass. Depending on the location of your blockages and your general health, you have several options for where the bypass begins and concludes.
This procedure widens the damaged section of your arteries and increases blood flow. Your stent can be inserted using endovascular (minimally invasive) techniques by your physician.

