VARICOSE VEINS
Varicose veins are enlarged, twisted, and often bulging veins that commonly occur in the legs and feet. They are a type of venous disorder that can be both a cosmetic concern and a potential medical issue. Here's an overview of varicose veins, including their symptoms, causes, and treatment options:
Symptoms:
Varicose veins can cause a range of symptoms, including:
- Visible Veins: Bulging, twisted, or rope-like veins that are visible on the skin's surface, usually in the legs or feet.
- Pain or Aching: Discomfort, heaviness, or aching in the legs, especially after prolonged periods of standing or sitting.
- Swelling: Swelling in the lower legs and ankles.
- Throbbing or Burning: Sensations of throbbing, burning, or itching in the affected area.
- Leg Cramps: Occasional cramps or muscle spasms in the legs, particularly at night.
- Skin Changes: Changes in skin color, texture, or appearance around the affected veins, including darkening or inflammation.
- Ulcers: In more severe cases, varicose veins can lead to skin ulcers, especially near the ankles.
Causes:
Varicose veins develop due to the weakening and malfunctioning of the valves within the veins that help blood flow against gravity back to the heart. When these valves fail, blood can pool in the veins, causing them to enlarge and become varicose. Several factors contribute to the development of varicose veins:
- Heredity: A family history of varicose veins increases the risk of developing them.
- Age: The risk of varicose veins tends to increase with age.
- Gender: Women are more likely than men to develop varicose veins.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes and increased pressure on the veins during pregnancy can contribute to varicose veins.
- Obesity: Excess weight puts added pressure on the veins.
- Prolonged Standing or Sitting: Jobs or activities that require long periods of standing or sitting can contribute to the development of varicose veins.
- Lack of Movement: A sedentary lifestyle can impact blood circulation and vein health.
Treatment:
The treatment of varicose veins depends on their severity, symptoms, and the presence of complications. Treatment options include:
- Lifestyle Changes: Engaging in regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy weight, and avoiding prolonged periods of sitting or standing can help improve vein health.
- Compression Stockings: Wearing compression stockings provides external support to the veins, helping to improve blood flow and reduce discomfort.
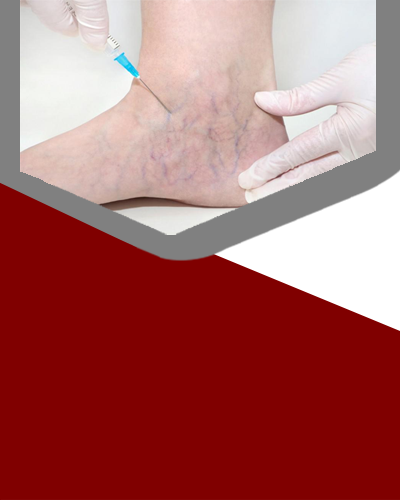
- Sclerotherapy: This minimally invasive procedure involves injecting a solution into the varicose veins to close them off and redirect blood flow to healthier veins.
- Endovenous Laser Treatment (EVLT) or Radiofrequency Ablation (RFA): These procedures use laser or radiofrequency energy to close off and seal varicose veins.
- Surgical Procedures: Surgical options, such as vein stripping or ligation, may be considered for severe cases or when other treatments are not effective.
- Laser Therapy: Laser treatments can be used to treat smaller varicose veins and spider veins.
The choice of treatment depends on individual factors and should be discussed with a healthcare provider or vascular specialist. It's important to seek medical advice if you experience symptoms of varicose veins or have concerns about their appearance or impact on your health.